Tachycardia (faster beating heart)
-
Introduction
Tachycardia, a medical term describing a faster-than-normal heart rate, is a condition that can affect individuals of all ages. It occurs when the heart beats too quickly, potentially disrupting its normal rhythm and function. This article explores tachycardia, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and the importance of understanding and managing this condition.
Understanding Tachycardia
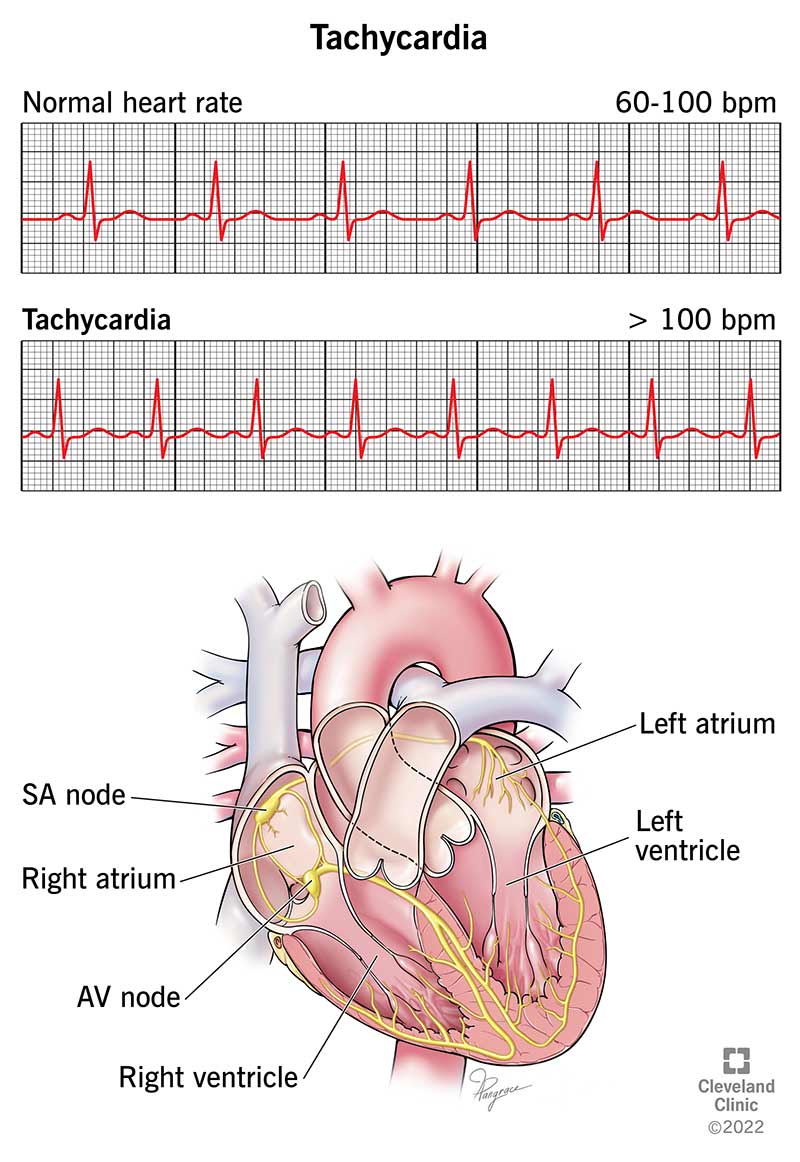
Tachycardia refers to a heart rate that exceeds the typical resting rate, which is approximately 60-100 beats per minute (bpm) for most adults. When the heart beats too rapidly, it may not have enough time to fill with blood between contractions, compromising its ability to pump blood effectively. This can lead to a range of symptoms and, in some cases, serious complications.
Causes and Risk Factors
Tachycardia can have various causes, including:
- Stress and Anxiety: Emotional or psychological stress can temporarily increase heart rate.
- Fever: Elevated body temperature can lead to tachycardia.
- Anemia: A reduced number of red blood cells can affect oxygen delivery to tissues and increase heart rate.
- Dehydration: Inadequate fluid levels can result in electrolyte imbalances that affect heart rhythm.
- Heart Conditions: Conditions like atrial fibrillation (AFib), atrial flutter, or ventricular tachycardia can cause rapid heart rates.
- Medications and Stimulants: Certain drugs, caffeine, and stimulants can trigger tachycardia.
- Medical Conditions: Hyperthyroidism, high blood pressure, and heart disease can contribute to tachycardia.
Symptoms
The symptoms of tachycardia can vary depending on the underlying cause and the individual’s overall health. Common symptoms include:
- Palpitations: Feeling a racing, pounding, or fluttering sensation in the chest.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Often accompanied by a feeling of unsteadiness.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity.
- Chest Pain: Discomfort or pain in the chest, which can be mistaken for a heart attack.
- Fatigue: Unexplained tiredness and weakness.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing tachycardia typically involves a series of tests and evaluations, such as:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): Records the heart’s electrical activity, identifying irregular rhythms.
- Holter Monitor: A portable ECG device worn for 24-48 hours to monitor heart rhythms continuously.
- Blood Tests: To check for underlying medical conditions or electrolyte imbalances.
- Exercise Stress Test: Measures heart rate and rhythm during physical activity.
- Echocardiogram: Uses sound waves to visualize the heart’s structure and function.
Treatment Options
The approach to treating tachycardia depends on its cause, severity, and impact on the individual’s quality of life. Treatment options may include:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Managing stress, staying hydrated, and limiting caffeine and alcohol intake.
- Medications: Antiarrhythmic drugs or beta-blockers to control heart rate and rhythm.
- Catheter Ablation: A minimally invasive procedure to treat abnormal electrical pathways in the heart.
- Pacemaker: Implanted to regulate heart rate in certain cases.
- Cardioversion: Electrical shock therapy to restore normal heart rhythm.
Importance of Understanding and Managing Tachycardia
Recognizing the signs of tachycardia and seeking medical attention promptly is crucial. Untreated tachycardia can lead to serious complications, including blood clots, stroke, heart failure, and sudden cardiac arrest. Managing the condition effectively, either through lifestyle changes or medical interventions, can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with tachycardia.
Conclusion
Tachycardia, characterized by a faster-than-normal heart rate, is a condition that requires attention and appropriate management. Understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms, and seeking medical advice are essential steps toward maintaining a healthy heart rhythm. By doing so, individuals can navigate the challenges of tachycardia and work toward a balanced and heart-healthy life.
