Insulin Failed?
Introduction
Insulin is a vital hormone produced by the pancreas, playing a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels. When insulin fails or becomes ineffective, it can lead to a range of health complications, most notably diabetes. This article delves into the concept of insulin failure, its causes, consequences, management strategies, and the importance of blood sugar control.
Understanding Insulin Failure
Insulin failure refers to the inability of the body to utilize insulin effectively or produce it in sufficient quantities. It is most commonly associated with two major forms of diabetes:
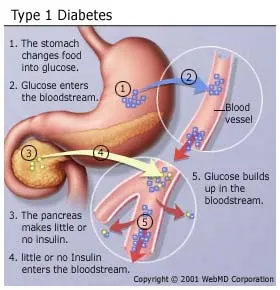
- Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This results in an absolute insulin deficiency.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Typically develops when the body’s cells become resistant to the effects of insulin, requiring the pancreas to produce more insulin to maintain blood sugar control. Over time, the pancreas may struggle to keep up with the demand, resulting in relative insulin deficiency.
Causes of Insulin Failure
- Type 1 Diabetes: The exact cause is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors, including viral infections and immune system abnormalities.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Insulin resistance often results from lifestyle factors, such as obesity, physical inactivity, and poor dietary choices. Genetics can also play a role.
Consequences of Insulin Failure
When insulin fails to perform its regulatory function, several health complications can arise, including:
- Hyperglycemia: Elevated blood sugar levels can lead to immediate symptoms like excessive thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue.
- Hypoglycemia: Insufficient insulin can cause dangerously low blood sugar levels, resulting in confusion, dizziness, and even loss of consciousness.
- Long-Term Complications: Prolonged periods of uncontrolled blood sugar can damage blood vessels, nerves, and vital organs, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, vision problems, and neuropathy.
Management Strategies
Managing insulin failure involves strategies tailored to the specific type of diabetes and its severity:
- Type 1 Diabetes Management:
- Insulin Therapy: Individuals with type 1 diabetes require daily insulin injections or insulin pump therapy to replace the missing hormone.
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Frequent blood glucose checks help adjust insulin doses.
- Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management are crucial.
- Type 2 Diabetes Management:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Weight management, healthy eating, and physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity.
- Oral Medications: Some people with type 2 diabetes may require oral medications to enhance insulin action.
- Insulin Therapy: In advanced cases, insulin may be prescribed.
Importance of Blood Sugar Control
Effective management of insulin failure through blood sugar control is paramount in preventing complications. Consistently high or low blood sugar levels can have detrimental effects on overall health and quality of life. Monitoring blood sugar, adhering to prescribed treatments, and making healthy lifestyle choices are vital steps toward achieving optimal control.
Conclusion
Insulin failure is a complex issue with far-reaching consequences. Understanding the causes, consequences, and management strategies is essential for individuals living with diabetes or at risk of developing it. By embracing a proactive approach to blood sugar control, individuals can mitigate the effects of insulin failure and work toward a healthier, more fulfilling life.
